Sunday, 22 March 2015
Friday, 6 March 2015
Making Windows 7 Bootable USB - Using CMD
Creating a usb pendrive using command prompt is not hard, it is one of the most common ways to create a bootable usb.
This method does not work if your operating sistem is windows xp or windows 8 , you cannot select the primary partition in comand prompt.
You just need to follow these simple steps:
This method does not work if your operating sistem is windows xp or windows 8 , you cannot select the primary partition in comand prompt.
You just need to follow these simple steps:
- First step is to obtain the windows files from somewhere and save them to a folder in your pc. You can rip a windows dvd , or if you have the iso image file you can open it with magic disc or daemon tools or even winrar , and you need to copy the whole content to a folder anywhere in your pc , you just need to make sure you know where it is located.
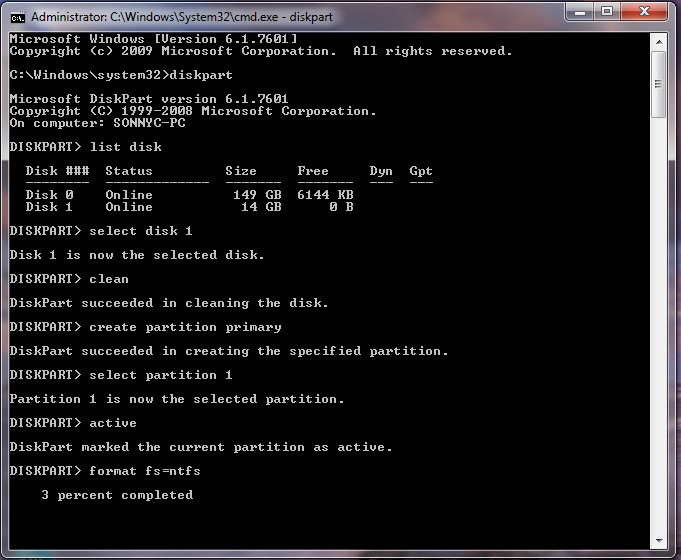
- Make sure your usb stick is inserted, go to start search cmd , right click the file and select run as administrator. The command prompt will appear, now you need to write the following comands:
- diskpart→list disk→select disk 1(chose the usb device, you will recognize it by its size)→clean(this will erase the usb)→create partition primary→select partition 1→active→format fs=ntfs(this will format the usb drive and will take 10-15 minutes)→
- After the format is done you have to continue writting in command promt : →assign(now you will notice that the usb drive changed its letter to (H): or (G))→exit(this command will exit the disk part function)
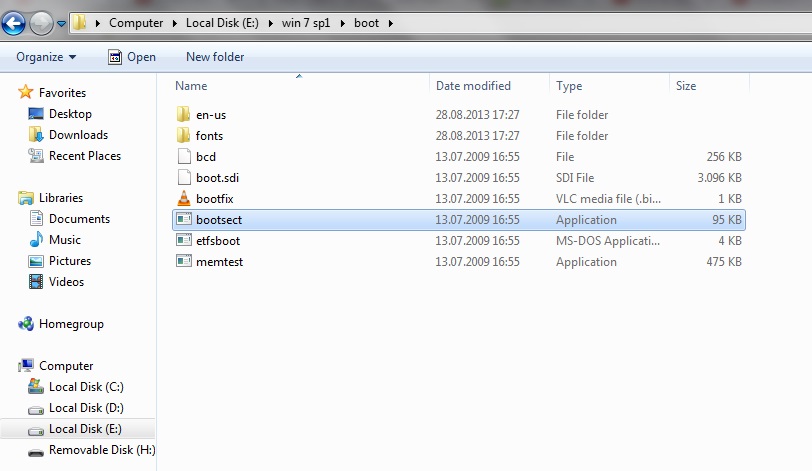
- Now you have to write the path to the executable file in your
windows saved folder , make sure that in your windows folder you have
the boot folder with the bootsect executable file.
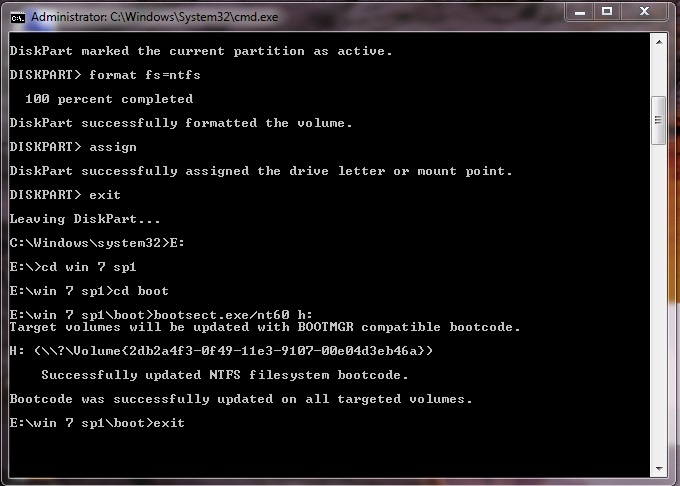
- In my case the command goes like this: E:→cd win 7 sp1→

- Now you have to copy all the files in the windows folder to your usb drive.
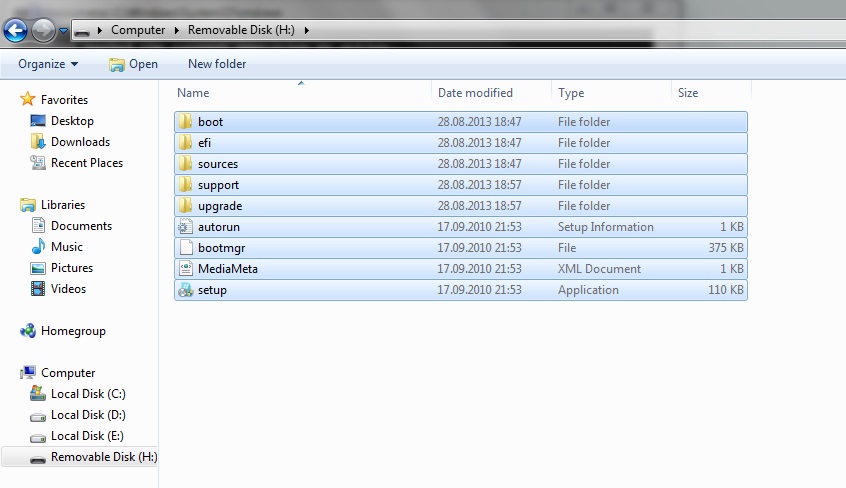
- ALL DONE. You can now restart your pc and boot from the usb hard drive.
Wednesday, 4 March 2015
Iron Man - Pc Game
Download This Game
 Iron Man Game System Requirements
Iron Man Game System Requirements
> Operating System : Windows XP/Windows 7/Windows 8 and 8.1
> Processor : Dual Core 1.9 GHz
> Ram : 1GB
> Hard Disk Space : 6 GB
>Size : 206.33 MB
Command Prompt Basics - A Getting Started Guide
Many of the troubleshooting techniques you will find on the internet
make use of the DOS or Command Prompt. This is how computers used to
work before the mouse became common. You have to type in your commands.
This site will give you a quick overview of how the command prompt
works. Initially it starts with showing you how to move around your file
system. When it comes to running more advanced commands, this basic
information will help because different commands need to be run from
different directories.
This information was formally on amset.info, but has now been moved to its own separate domain. You may have been redirected here from amset.info.
Throughout this page you will see this referred to as a command prompt. DOS Prompt and Command Prompt are the same thing.
You should have a Command Prompt open when reading this page so that you can try the commands. Unless stated, you will not damage your data by just moving around your folders.
Opening a Command Prompt
There are two conventional ways to start a Command prompt.
The screenshot below shows a Command Prompt on Windows 7 - it is almost identical on all other versions of Windows.

Command Prompt on Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 2008
On Windows Vista and Windows 7, a standard Command Prompt may not allow you to do everything that you need to. In that case you will need to use an elevated command prompt.
The best way to start an elevated command prompt is to RIGHT click on the shortcut and choose Run As Administrator.
How to tell if the command prompt is elevated
If the prompt is elevated, then the initial path will be C:\Windows\System32. The title bar will also say "Administrator: Command Prompt". If the prompt is not elevated then by default it will start in C:\Users\Username (where username is the username of the account in use) and the title bar will just say "Command Prompt". The example above was configured to start in C:\ .

Closing a command prompt
You can close a command prompt either by clicking on the cross in the corner, typing exit and pressing enter, or choosing Close when right clicking the Command Prompt icon on the task bar.
However command history is not maintained across sessions, so if you have a lengthy command that you want to use again, it needs to be copied out.
Command Prompt Basics
When you are working in Command Prompt, there are a couple of things that usually work:
Many of the commands will have extra options available, known as switches. They are added to the command by entering a "/" then a letter, number or word. These can change how the tool works or handles the information. A common switch would be the help command, which will also give you information on the other switches available.
"command" /?
This will usually bring up information about the command and the available switches. If it doesn't work, try "-?" after the command instead.
"command" > "filename.txt"
This will send the results of the command to a text file instead of the screen. You can include switches as well. This is particularly useful if you are looking at the help information for a command. Look at this example command:
xcopy /? >c:\xcopy.txt
This writes the content of the help command to a file called xcopy.txt located in the root of the C:\ drive.
Stopping a Command
If you start a command it appears to be looping, showing more than you expect, then you can stop it sing the key combination CTRL-C.
If you are interested in simply allowing the text to show, but a screen at a time, then you should use the MORE command.
Copy and Pasting a command in to the window
The first thing to note, which will usually catch newcomers to the Command Prompt out, is that the usual CTRL-C and CTRL-V commands will not work for a command prompt window.
Copying Text
To copy text, such as a long command that you have been using or the results of a command, click on the icon in the top LEFT corner, and then choose Edit, and Mark.

The cursor will then change. You can then use the mouse to highlight the text that you want to copy. Once you have done so, press enter. The highlight will disappear, and the text will be copied in to the clipboard. You can then copy it elsewhere, or in to the same Command Prompt Window.
Pasting Text
To paste text, move the cursor to the point where you want to enter it, using the cursor keys. Then click on the icon in the top left corner and choose Edit, Paste.
CLS
If you have lots of text in your Command Prompt window, this command will clear it. The history of previous commands typed in that session will be maintained.
Moving Between Folders, Listing Folder Contents
There are two commands you will use most
The "Dir" command is probably the most basic command. It gives you a listing of all the files and folders that are located in the folder that you are currently open in.
For example, in the screenshot above, we are in the root of the C:\ drive. If a DIR command is carried out at this point, then you will get a result similar to this:
Volume in drive C is System
Volume Serial Number is 1234-5678
Directory of C:\
25/10/2002 23:42 0 AUTOEXEC.BAT
26/10/2002 01:03 0 COMLOG.txt
25/10/2002 23:42 0 CONFIG.SYS
06/02/2003 15:08 0 dir.txt
04/11/2002 20:40 262,144 ntuser.dat
25/10/2002 23:49 <DIR> Documents and Settings
27/01/2003 19:58 <DIR> Program Files
27/01/2003 09:26 <DIR> WINDOWS
5 File(s) 262,144 bytes
3 Dir(s) 12,528,111,616 bytes free
This command does not show you any hidden files. To see hidden files you will need to use the ATTRIB command.
Advanced "dir" commands
You can get a little more advanced with the dir command by putting extra commands after the intitial "dir".
For example:
dir /s
will show the contents of the current folder, and any subfolders that are below. This will produce a very long file listing. You might want to filter the results or send them to a text file (see above).
dir /s something.doc
This command will search through all subdirectories below for a file that matches that file name. Similarly, issuing the command
dir /s *.doc
will list all files that end in .doc (Word files).
More information on the DIR command can be found in the DIR Command Reference.
CD - Change Directory
The CD command is very simple to use. All commands are relative to the directory that you are in. Therefore, using the example output of a "dir" that is shown above, if you want to change to the "Windows" directory, you would type
CD Windows
If you want to change to the "system" directory (which is a sub directory of "windows"), you would enter
CD System
However if you knew that you wanted to change to the system directory immediately, you could type this command instead:
CD Windows\System
However if you were already deep in another directory (for example c:\ documents and settings \username\ local settings) and then wanted to move directly to windows\system then you can do that by putting in an initial backwards slash:
CD \Windows\System
This tells the command to go to the root of the drive, then to the directory Windows and system.
Moving Back Up
You can also move back up the tree, instead of down.
If you want to just return to the root of the drive (C:\) you would just type
cd \ or cd\
If you wanted to just go back one level (to use the earlier example, you were in c:\windows\system and you wanted to be in c:\windows) you would just type:
cd..
Alternatively, if you want to access a totally different directory, for example "Program Files" you could type
cd program files or cd "program files"
When typing directories to change to, if the directory name is unique, then you can use wild cards. For example
cd program*
Directory Entry Shortcut: : If you are on Windows 2000 or XP and you have a Windows Explorer screen open at the location that you want to run a Command Prompt command you could open the Command Prompt and typing a long series of directories or CD commands. Instead, just type CD and then a space, then drag and drop the directory you want to work in to the Command Prompt window. The full path to the directory will be entered, ready for you to press enter.
More information on the CD command can be found in the CD Command Reference.
Change Drive
If you want to run a command against a directory on another drive, such as the D drive, then you need to change to that drive, This is done simply by entering the drive letter and a colon:
d:
On Windows Vista and higher you can also combine the drive letter change and directory by using the full path:
cd d:\downloads
On Windows XP and older, you can still enter the above command, but will then need to do d: . When you do, you will find that you are in the directory where you did the CD command to.
File Renaming
You can rename files in a command prompt.
rename something.txt someone.txt
would rename the file something.txt to someone.txt
Full Rename Command Reference.
Directory Creation
You can create directories from the command prompt:
mkdir something
would create a directory called "something".
If you want a directory with a name that has a space in it, such as "My Files" you need include the command in " ":
mkdir "my files"
This ensures that the directory is created with the space. Without the space you will get a new directory called "my" and an error message.
You can also use the md command instead of mkdir.
Windows Power Toys
If you do a lot of work in the command prompt, then you might be interested in installing the "Command Prompt Here" (Windows 9x, NT and 2000) or "Command Here" (Windows XP) Power Toys. These add a new command the right click menu you get when you click on a directory allowing you to open a Command Prompt in that directory.
You can download these Power Toys from Microsoft's web site.
Changing where the Command Prompt shortcut starts
By default, the command prompt will start in your Home directory. This could be "C:\Documents and Settings\Username" or a network drive. If you want to always start in another location, such as the root of the C: drive, then you can change the Shortcut. Right click on it and choose Properties. Change the value in "Start In" to your preferred location.
Keyboard Short Cuts
There are a couple of shortcuts that you can use from the keyboard instead of typing full directory paths.
Use a Wild Card
If the directory you are wanting to change to is very long but uniquely named, then you can use a wild card instead of typing the entire thing.
For example, instead of:
cd "program files"
you could enter
cd prog*
Enter the wildcard character once you have typed enough characters for Windows to only have one choice.
Using "Tab" to Select Files or Folders - Windows XP/Server 2003 only
Another neat trick if you are using a command prompt on Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 and is to use the "Tab" key to scroll through the files and folders in the current directory. Type the command you want to use as normal, for example "cd" then press tab to cycle through the files and folders until you reach the one you want. Then press enter. You may still have to enter the " as before, so would type " cd " " then press tab until you reached the folder you want to change to, enter the second " to finish off and press enter.
This technique can save a lot of time if you need to change to a directory with a long name.
It will also let you enter hidden folders that do not appear with dir without having to remember the correct name.
Repeat a Command
If you want to repeat a command that you have just run, or adjust something in the last command, press the "Up" cursor key to bring it back. You can then adjust it and press enter. Useful if you are trying to work out what switches and options you can use to achieve a certain result. History is not maintained across sessions, but is maintained if you use CLS to clear the screen.
Full Listing of Commands and their Options.
If you want a full list of the commands available to you, just type "help" and they will be listed. You can then type "help <command>" for the instructions.
Similarly, typing /? after the command will also bring up the full list of options available for that command.
A complete list of the built in Commands, along with examples and notes on their use can be found here.
Screen Size and Buffer Size
When you are working with a Command Prompt, it maybe helpful to increase the screen size or the buffer size.
Screen size is what you can actually see on the screen.
Buffer size is what is stored and can be viewed by using the scroll bars at the side.
To change the screen size and buffer size, right click on the icon in the top left corner of the Command Prompt window and choose Properties. Then click on layout.
A good buffer size is height 300, whereas a good screen size is height between 25 and 50.
After pressing OK you will be asked if you want to apply the changes to the shortcut or the current window only. If you are testing, select the current window only.
Deleting Files and Folders
If you want to delete a file, then just type:
del filename.ext
If you want to delete all files in a folder then type
del *.*
similarly if you want to delete all files with a certain extension, then type
del *.ext
(where ext is the extension you want to delete)
To delete a folder, simply enter
del foldername
There are more advanced options for deleting files through the Command Prompt - view the Command Reference for DEL to see the full list.
Note - if you delete a file within a Command Prompt session it does not go in to the recycle bin. It will be deleted immediately.
Advanced Tasks
The command line allows you to more advanced tasks, either using built in tools or additional third party tools. This can include network diagnostics, Email MX record lookup and identifying what your computer is doing with the network or internet.
This information was formally on amset.info, but has now been moved to its own separate domain. You may have been redirected here from amset.info.
Throughout this page you will see this referred to as a command prompt. DOS Prompt and Command Prompt are the same thing.
You should have a Command Prompt open when reading this page so that you can try the commands. Unless stated, you will not damage your data by just moving around your folders.
Opening a Command Prompt
There are two conventional ways to start a Command prompt.
- Start, Programs, Accessories, Command prompt
- Start, Run and type "cmd" (minus quotes) and press enter.
The screenshot below shows a Command Prompt on Windows 7 - it is almost identical on all other versions of Windows.

Command Prompt on Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 2008
On Windows Vista and Windows 7, a standard Command Prompt may not allow you to do everything that you need to. In that case you will need to use an elevated command prompt.
The best way to start an elevated command prompt is to RIGHT click on the shortcut and choose Run As Administrator.
How to tell if the command prompt is elevated
If the prompt is elevated, then the initial path will be C:\Windows\System32. The title bar will also say "Administrator: Command Prompt". If the prompt is not elevated then by default it will start in C:\Users\Username (where username is the username of the account in use) and the title bar will just say "Command Prompt". The example above was configured to start in C:\ .

Closing a command prompt
You can close a command prompt either by clicking on the cross in the corner, typing exit and pressing enter, or choosing Close when right clicking the Command Prompt icon on the task bar.
However command history is not maintained across sessions, so if you have a lengthy command that you want to use again, it needs to be copied out.
Command Prompt Basics
When you are working in Command Prompt, there are a couple of things that usually work:
Many of the commands will have extra options available, known as switches. They are added to the command by entering a "/" then a letter, number or word. These can change how the tool works or handles the information. A common switch would be the help command, which will also give you information on the other switches available.
"command" /?
This will usually bring up information about the command and the available switches. If it doesn't work, try "-?" after the command instead.
"command" > "filename.txt"
This will send the results of the command to a text file instead of the screen. You can include switches as well. This is particularly useful if you are looking at the help information for a command. Look at this example command:
xcopy /? >c:\xcopy.txt
This writes the content of the help command to a file called xcopy.txt located in the root of the C:\ drive.
Stopping a Command
If you start a command it appears to be looping, showing more than you expect, then you can stop it sing the key combination CTRL-C.
If you are interested in simply allowing the text to show, but a screen at a time, then you should use the MORE command.
Copy and Pasting a command in to the window
The first thing to note, which will usually catch newcomers to the Command Prompt out, is that the usual CTRL-C and CTRL-V commands will not work for a command prompt window.
Copying Text
To copy text, such as a long command that you have been using or the results of a command, click on the icon in the top LEFT corner, and then choose Edit, and Mark.

The cursor will then change. You can then use the mouse to highlight the text that you want to copy. Once you have done so, press enter. The highlight will disappear, and the text will be copied in to the clipboard. You can then copy it elsewhere, or in to the same Command Prompt Window.
Pasting Text
To paste text, move the cursor to the point where you want to enter it, using the cursor keys. Then click on the icon in the top left corner and choose Edit, Paste.
CLS
If you have lots of text in your Command Prompt window, this command will clear it. The history of previous commands typed in that session will be maintained.
Moving Between Folders, Listing Folder Contents
There are two commands you will use most
- "CD" (change directory) (minus quotes). This changes directory relevant to the one you are currently working in.
- "DIR" (directory) (minus quotes). This lists the files and directories in the folder that you are in.
The "Dir" command is probably the most basic command. It gives you a listing of all the files and folders that are located in the folder that you are currently open in.
For example, in the screenshot above, we are in the root of the C:\ drive. If a DIR command is carried out at this point, then you will get a result similar to this:
Volume in drive C is System
Volume Serial Number is 1234-5678
Directory of C:\
25/10/2002 23:42 0 AUTOEXEC.BAT
26/10/2002 01:03 0 COMLOG.txt
25/10/2002 23:42 0 CONFIG.SYS
06/02/2003 15:08 0 dir.txt
04/11/2002 20:40 262,144 ntuser.dat
25/10/2002 23:49 <DIR> Documents and Settings
27/01/2003 19:58 <DIR> Program Files
27/01/2003 09:26 <DIR> WINDOWS
5 File(s) 262,144 bytes
3 Dir(s) 12,528,111,616 bytes free
This command does not show you any hidden files. To see hidden files you will need to use the ATTRIB command.
Advanced "dir" commands
You can get a little more advanced with the dir command by putting extra commands after the intitial "dir".
For example:
dir /s
will show the contents of the current folder, and any subfolders that are below. This will produce a very long file listing. You might want to filter the results or send them to a text file (see above).
dir /s something.doc
This command will search through all subdirectories below for a file that matches that file name. Similarly, issuing the command
dir /s *.doc
will list all files that end in .doc (Word files).
More information on the DIR command can be found in the DIR Command Reference.
CD - Change Directory
The CD command is very simple to use. All commands are relative to the directory that you are in. Therefore, using the example output of a "dir" that is shown above, if you want to change to the "Windows" directory, you would type
CD Windows
If you want to change to the "system" directory (which is a sub directory of "windows"), you would enter
CD System
However if you knew that you wanted to change to the system directory immediately, you could type this command instead:
CD Windows\System
However if you were already deep in another directory (for example c:\ documents and settings \username\ local settings) and then wanted to move directly to windows\system then you can do that by putting in an initial backwards slash:
CD \Windows\System
This tells the command to go to the root of the drive, then to the directory Windows and system.
Moving Back Up
You can also move back up the tree, instead of down.
If you want to just return to the root of the drive (C:\) you would just type
cd \ or cd\
If you wanted to just go back one level (to use the earlier example, you were in c:\windows\system and you wanted to be in c:\windows) you would just type:
cd..
Alternatively, if you want to access a totally different directory, for example "Program Files" you could type
cd program files or cd "program files"
When typing directories to change to, if the directory name is unique, then you can use wild cards. For example
cd program*
Directory Entry Shortcut: : If you are on Windows 2000 or XP and you have a Windows Explorer screen open at the location that you want to run a Command Prompt command you could open the Command Prompt and typing a long series of directories or CD commands. Instead, just type CD and then a space, then drag and drop the directory you want to work in to the Command Prompt window. The full path to the directory will be entered, ready for you to press enter.
More information on the CD command can be found in the CD Command Reference.
Change Drive
If you want to run a command against a directory on another drive, such as the D drive, then you need to change to that drive, This is done simply by entering the drive letter and a colon:
d:
On Windows Vista and higher you can also combine the drive letter change and directory by using the full path:
cd d:\downloads
On Windows XP and older, you can still enter the above command, but will then need to do d: . When you do, you will find that you are in the directory where you did the CD command to.
File Renaming
You can rename files in a command prompt.
rename something.txt someone.txt
would rename the file something.txt to someone.txt
Full Rename Command Reference.
Directory Creation
You can create directories from the command prompt:
mkdir something
would create a directory called "something".
If you want a directory with a name that has a space in it, such as "My Files" you need include the command in " ":
mkdir "my files"
This ensures that the directory is created with the space. Without the space you will get a new directory called "my" and an error message.
You can also use the md command instead of mkdir.
Windows Power Toys
If you do a lot of work in the command prompt, then you might be interested in installing the "Command Prompt Here" (Windows 9x, NT and 2000) or "Command Here" (Windows XP) Power Toys. These add a new command the right click menu you get when you click on a directory allowing you to open a Command Prompt in that directory.
You can download these Power Toys from Microsoft's web site.
Changing where the Command Prompt shortcut starts
By default, the command prompt will start in your Home directory. This could be "C:\Documents and Settings\Username" or a network drive. If you want to always start in another location, such as the root of the C: drive, then you can change the Shortcut. Right click on it and choose Properties. Change the value in "Start In" to your preferred location.
Keyboard Short Cuts
There are a couple of shortcuts that you can use from the keyboard instead of typing full directory paths.
Use a Wild Card
If the directory you are wanting to change to is very long but uniquely named, then you can use a wild card instead of typing the entire thing.
For example, instead of:
cd "program files"
you could enter
cd prog*
Enter the wildcard character once you have typed enough characters for Windows to only have one choice.
Using "Tab" to Select Files or Folders - Windows XP/Server 2003 only
Another neat trick if you are using a command prompt on Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 and is to use the "Tab" key to scroll through the files and folders in the current directory. Type the command you want to use as normal, for example "cd" then press tab to cycle through the files and folders until you reach the one you want. Then press enter. You may still have to enter the " as before, so would type " cd " " then press tab until you reached the folder you want to change to, enter the second " to finish off and press enter.
This technique can save a lot of time if you need to change to a directory with a long name.
It will also let you enter hidden folders that do not appear with dir without having to remember the correct name.
Repeat a Command
If you want to repeat a command that you have just run, or adjust something in the last command, press the "Up" cursor key to bring it back. You can then adjust it and press enter. Useful if you are trying to work out what switches and options you can use to achieve a certain result. History is not maintained across sessions, but is maintained if you use CLS to clear the screen.
Full Listing of Commands and their Options.
If you want a full list of the commands available to you, just type "help" and they will be listed. You can then type "help <command>" for the instructions.
Similarly, typing /? after the command will also bring up the full list of options available for that command.
A complete list of the built in Commands, along with examples and notes on their use can be found here.
When you are working with a Command Prompt, it maybe helpful to increase the screen size or the buffer size.
Screen size is what you can actually see on the screen.
Buffer size is what is stored and can be viewed by using the scroll bars at the side.
To change the screen size and buffer size, right click on the icon in the top left corner of the Command Prompt window and choose Properties. Then click on layout.
A good buffer size is height 300, whereas a good screen size is height between 25 and 50.
After pressing OK you will be asked if you want to apply the changes to the shortcut or the current window only. If you are testing, select the current window only.
Deleting Files and Folders
If you want to delete a file, then just type:
del filename.ext
If you want to delete all files in a folder then type
del *.*
similarly if you want to delete all files with a certain extension, then type
del *.ext
(where ext is the extension you want to delete)
To delete a folder, simply enter
del foldername
There are more advanced options for deleting files through the Command Prompt - view the Command Reference for DEL to see the full list.
Note - if you delete a file within a Command Prompt session it does not go in to the recycle bin. It will be deleted immediately.
Advanced Tasks
The command line allows you to more advanced tasks, either using built in tools or additional third party tools. This can include network diagnostics, Email MX record lookup and identifying what your computer is doing with the network or internet.
CMD All Commands
An A-Z Index of the Windows CMD command line
ADDUSERS Add or list users to/from a CSV file ADmodcmd Active Directory Bulk Modify ARP Address Resolution Protocol ASSOC Change file extension associations• ASSOCIAT One step file association AT Schedule a command to run at a specific time ATTRIB Change file attributes b BCDBOOT Create or repair a system partition BCDEDIT Manage Boot Configuration Data BITSADMIN Background Intelligent Transfer Service BOOTCFG Edit Windows boot settings BROWSTAT Get domain, browser and PDC info c CACLS Change file permissions CALL Call one batch program from another• CERTREQ Request certificate from a certification authority CERTUTIL Utility for certification authority (CA) files and services CD Change Directory - move to a specific Folder• CHANGE Change Terminal Server Session properties CHKDSK Check Disk - check and repair disk problems CHKNTFS Check the NTFS file system CHOICE Accept keyboard input to a batch file CIPHER Encrypt or Decrypt files/folders CleanMgr Automated cleanup of Temp files, recycle bin CLIP Copy STDIN to the Windows clipboard CLS Clear the screen• CMD Start a new CMD shell CMDKEY Manage stored usernames/passwords COLOR Change colors of the CMD window• COMP Compare the contents of two files or sets of files COMPACT Compress files or folders on an NTFS partition COMPRESS Compress one or more files CONVERT Convert a FAT drive to NTFS COPY Copy one or more files to another location• CSCcmd Client-side caching (Offline Files) CSVDE Import or Export Active Directory data d DATE Display or set the date• DEFRAG Defragment hard drive DEL Delete one or more files• DELPROF Delete user profiles DELTREE Delete a folder and all subfolders DevCon Device Manager Command Line Utility DIR Display a list of files and folders• DIRQUOTA File Server Resource Manager Disk quotas DIRUSE Display disk usage DISKPART Disk Administration DISKSHADOW Volume Shadow Copy Service DISKUSE Show the space used in folders DOSKEY Edit command line, recall commands, and create macros DriverQuery Display installed device drivers DSACLs Active Directory ACLs DSAdd Add items to active directory (user group computer) DSGet View items in active directory (user group computer) DSQuery Search for items in active directory (user group computer) DSMod Modify items in active directory (user group computer) DSMove Move an Active directory Object DSRM Remove items from Active Directory e ECHO Display message on screen• ENDLOCAL End localisation of environment changes in a batch file• ERASE Delete one or more files• EVENTCREATE Add a message to the Windows event log EXIT Quit the current script/routine and set an errorlevel• EXPAND Uncompress CAB files EXTRACT Uncompress CAB files f FC Compare two files FIND Search for a text string in a file FINDSTR Search for strings in files FOR /F Loop command: against a set of files• FOR /F Loop command: against the results of another command• FOR Loop command: all options Files, Directory, List• FORFILES Batch process multiple files FORMAT Format a disk FREEDISK Check free disk space FSUTIL File and Volume utilities FTP File Transfer Protocol FTYPE File extension file type associations• g GETMAC Display the Media Access Control (MAC) address GOTO Direct a batch program to jump to a labelled line• GPRESULT Display Resultant Set of Policy information GPUPDATE Update Group Policy settings h HELP Online Help HOSTNAME Display the host name of the computer i iCACLS Change file and folder permissions IEXPRESS Create a self extracting ZIP file archive IF Conditionally perform a command• IFMEMBER Is the current user a member of a group IPCONFIG Configure IP INUSE Replace files that are in use by the OS l LABEL Edit a disk label LOGMAN Manage Performance Monitor logs LOGOFF Log a user off LOGTIME Log the date and time in a file m MAKECAB Create .CAB files MAPISEND Send email from the command line MBSAcli Baseline Security Analyzer MEM Display memory usage MD Create new folders• MKLINK Create a symbolic link (linkd) • MODE Configure a system device COM/LPT/CON MORE Display output, one screen at a time MOUNTVOL Manage a volume mount point MOVE Move files from one folder to another• MOVEUSER Move a user from one domain to another MSG Send a message MSIEXEC Microsoft Windows Installer MSINFO32 System Information MSTSC Terminal Server Connection (Remote Desktop Protocol) n NET Manage network resources NETDOM Domain Manager NETSH Configure Network Interfaces, Windows Firewall & Remote access NBTSTAT Display networking statistics (NetBIOS over TCP/IP) NETSTAT Display networking statistics (TCP/IP) NLSINFO Display locale information (reskit). NLTEST Network Location Test (AD) NOW Display the current Date and Time NSLOOKUP Name server lookup NTBACKUP Backup folders to tape NTDSUtil Active Directory Domain Services management NTRIGHTS Edit user account rights NVSPBIND Modify network bindings o OPENFILES Query or display open files p PATH Display or set a search path for executable files• PATHPING Trace route plus network latency and packet loss PAUSE Suspend processing of a batch file and display a message• PERMS Show permissions for a user PERFMON Performance Monitor PING Test a network connection POPD Return to a previous directory saved by PUSHD• PORTQRY Display the status of ports and services POWERCFG Configure power settings PRINT Print a text file PRINTBRM Print queue Backup/Recovery PRNCNFG Configure or rename a printer PRNMNGR Add, delete, list printers and printer connections ProcDump Monitor an application for CPU spikes PROMPT Change the command prompt• PsExec Execute process remotely PsFile Show files opened remotely PsGetSid Display the SID of a computer or a user PsInfo List information about a system PsKill Kill processes by name or process ID PsList List detailed information about processes PsLoggedOn Who's logged on (locally or via resource sharing) PsLogList Event log records PsPasswd Change account password PsPing Measure network performance PsService View and control services PsShutdown Shutdown or reboot a computer PsSuspend Suspend processes PUSHD Save and then change the current directory• q QGREP Search file(s) for lines that match a given pattern Query Process / QPROCESS Display processes Query Session / QWinsta Display all sessions (TS/Remote Desktop) Query TermServer /QAppSrv List all servers (TS/Remote Desktop) Query User / QUSER Display user sessions (TS/Remote Desktop) r RASDIAL Manage RAS connections RASPHONE Manage RAS connections RECOVER Recover a damaged file from a defective disk REG Registry: Read, Set, Export, Delete keys and values REGEDIT Import or export registry settings REGSVR32 Register or unregister a DLL REGINI Change Registry Permissions REM Record comments (remarks) in a batch file• REN Rename a file or files• REPLACE Replace or update one file with another Reset Session Delete a Remote Desktop Session RD Delete folder(s)• RMTSHARE Share a folder or a printer ROBOCOPY Robust File and Folder Copy ROUTE Manipulate network routing tables RUN Start | RUN commands RUNAS Execute a program under a different user account RUNDLL32 Run a DLL command (add/remove print connections) s SC Service Control SCHTASKS Schedule a command to run at a specific time SET Display, set, or remove session environment variables• SETLOCAL Control the visibility of environment variables• SetSPN Edit Service Principal Names SETX Set environment variables SFC System File Checker SHARE List or edit a file share or print share ShellRunAs Run a command under a different user account SHIFT Shift the position of batch file parameters• SHORTCUT Create a windows shortcut (.LNK file) SHUTDOWN Shutdown the computer SLEEP Wait for x seconds SLMGR Software Licensing Management (Vista/2008) SORT Sort input START Start a program, command or batch file• STRINGS Search for ANSI and UNICODE strings in binary files SUBINACL Edit file and folder Permissions, Ownership and Domain SUBST Associate a path with a drive letter SYSMON Monitor and log system activity to the Windows event log SYSTEMINFO List system configuration t TAKEOWN Take ownership of a file TASKLIST List running applications and services TASKKILL End a running process TELNET Communicate with another host using the TELNET protocol TIME Display or set the system time• TIMEOUT Delay processing of a batch file TITLE Set the window title for a CMD.EXE session• TLIST Task list with full path TOUCH Change file timestamps TRACERT Trace route to a remote host TREE Graphical display of folder structure TSDISCON Disconnect a Remote Desktop Session TSKILL End a running process TSSHUTDN Remotely shut down or reboot a terminal server TYPE Display the contents of a text file• TypePerf Write performance data to a log file TZUTIL Time Zone Utility v VER Display version information• VERIFY Verify that files have been saved• VOL Display a disk label• w W32TM Time Service WAITFOR Wait for or send a signal WEVTUTIL Clear event logs, enable/disable/query logs WHERE Locate and display files in a directory tree WHOAMI Output the current UserName and domain WINDIFF Compare the contents of two files or sets of files WINRM Windows Remote Management WINRS Windows Remote Shell WMIC WMI Commands WUAUCLT Windows Update x XCACLS Change file and folder permissions XCOPY Copy files and folders :: Comment / Remark•
VOIP - Free Call Using Internet

Step 1 : Go To https://www.freecall.com .
Step 2 : Click On "Desktop" For In Pc and Download ( You Also Click Another Devices If You Need)
Step 3 : After Downloading, Simply Just Install It. and Open
Step 4 : Create A account Fill All the Details Correctly.
Step 5 : Verify Your Email Id and Phone No. (Country Code Before Your Number Ex : +91xxxxxxxxxx)
Step 6 : Enjoy The Free Calls Over Internet.............. ( Only 2 Calls Free)
All Bollywood Movies Download Link - b/w Old to 2015
Download all Bollywood Movies Released Before 2015, 30 Feb .....
1 2 3:
A:
B:
C:
D:
E:
F:
G:
H:
I:
J:
K:
L:
M:
N:
O:
P:
Q:
R:
S:
T:
U:
V:
W:
X:
Y:
Z:
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)